Detailed explanation and analysis of the mechanism of action and clinical use of Guanfacine Hydrochloride Sustained-release Tablets
Guanfacine hydrochloride extended-release tablets (Guanfacine ER) is a selective α₂A- adrenergic receptor agonist. Its core mechanism is to improve attention, impulse control and executive functions by modulating neural signal transmission in the prefrontal cortex. The prefrontal cortex is an important area responsible for concentration and behavioral regulation, and is often in a state of low functional activity in patients with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Guanfacine enhances the stability of neural activity in this brain area, making signal transmission between neurons more orderly, and fundamentally improving distraction, over-impulsivity, and self-management abilities. In addition, it can also reduce the excitement of the sympathetic nervous system, so it has a certain effect of sedation, lowering heart rate and blood pressure, which is its key feature that distinguishes it from traditional stimulant ADHD drugs.
In terms of clinical indications, Guanfacine Hydrochloride Sustained-release Tablets are mainly used for the treatment of children and adolescents ADHD , especially for patients with poor tolerance to stimulant drugs, obvious anxiety, or tics. It can be used either as a single drug or in combination with stimulants such as methylphenidate and lisderamphetamine to enhance concentration and reduce impulsive behavior. Guanfacine has a relatively mild onset of action, and generally takes effect gradually after 1~2 weeks. The best effect is often after 4~6 weeks. Because the mechanism of action does not rely on dopamine enhancement, there is a lower risk of abuse and is suitable for adolescent patients who require long-term management of ADHD symptoms.
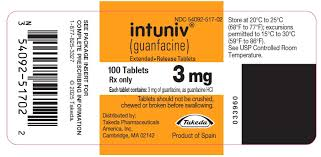
In terms of usage, guanfacine hydrochloride extended-release tablets should be taken orally once a day, usually in the morning or before going to bed. The tablet should be swallowed whole and avoid breaking or chewing to ensure stable release of the drug. The starting dose is usually 1mg, and the dose can be gradually increased every week based on efficacy and tolerance. The common maintenance dose is 2–4mg/ days. Doctors will adjust the dosage of stimulant drugs when using them together to avoid excessive sedation and hypotension. When stopping the drug, the dose needs to be gradually reduced, usually by 1 mg every 3–7 days to avoid rebound hypertension or increased heart rate caused by sudden drug withdrawal. This is an important step that requires special attention in clinical practice.
In terms of safety, the most common adverse reactions of guanfacine include Drowsiness, fatigue, hypotension, dizziness, dry mouth, and gastrointestinal discomfort etc., usually resolve as the body adapts. Because it may cause a decrease in heart rate or blood pressure, it is recommended to monitor blood pressure and heart rate during the initial treatment and dose adjustment period. Caution is required to avoid excessive sedation in patients receiving concomitant medications with sedating effects (e.g., antihistamines, benzodiazepines). If obvious drowsiness, syncope, or extreme fatigue occurs, you should contact your doctor promptly to adjust the dose. Overall, guanfacine hydrochloride sustained-release tablets have the advantages of safety, stable onset of effect, and low dependence in the management of ADHD. It is one of the important medication options for the long-term treatment of ADHD.
Reference materials:https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a694009.html
[ 免责声明 ] 本页面内容来自公开渠道(如FDA官网、Drugs官网、原研药厂官网等),仅供持有医疗专业资质的人员用于医学药学研究参考,不构成任何治疗建议或药品推荐。所涉药品可能未在中国大陆获批上市,不适用于中国境内销售和使用。如需治疗,请咨询正规医疗机构。本站不提供药品销售或代购服务。
.jpeg)


















